Abstract:
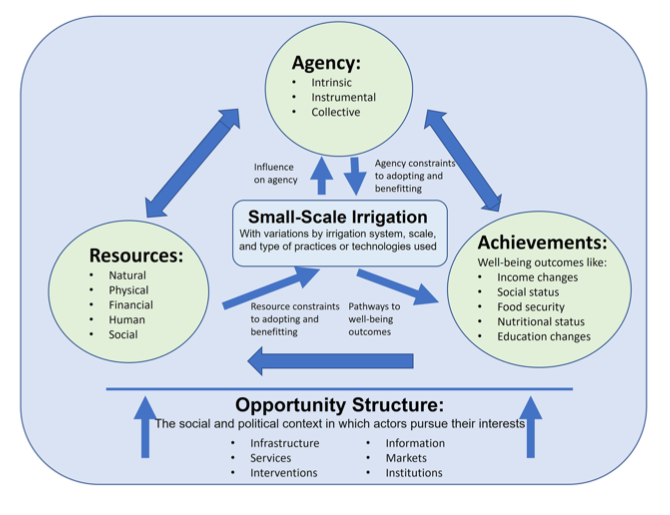
Women’s empowerment is often an important goal of development interventions. This paper explores local perceptions of empowerment in the Upper East Region of Ghana and the pathways through which small-scale irrigation intervention targeted to men and women farmers contributes to women’s empowerment. Using qualitative data collected with 144 farmers and traders through 28 individual interviews and 16 focus group discussions, this paper innovates a framework to integrate the linkages between small-scale irrigation and three dimensions of women’s empowerment: resources, agency, and achieve- ments. The relationship between the components of empowerment and small-scale irrigation are placed within a larger con- text of social change underlying these relationships. This shows that many women face serious constraints to participating in and benefitting from small-scale irrigation, including difficulties accessing land and water and gender norms that limit women’s ability to control farm assets. Despite these constraints, many women do benefit from participating in irrigated farming activities leading to an increase in their agency and well-being achievements. For some women, these benefits are indirect—these women allocate their time to more preferred activities when the household gains access to modern irrigation technology. The result is a new approach to understanding women’s empowerment in relation to irrigation technology.
Authors: Elizabeth Bryan and Elisabeth Garner
Source: Agriculture and Human Values
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10460-021-10291-1